Scikit-Learn implementa un total de 9 algoritmos de clustering diferentes. En el siguiente gráfico se muestra su comportamiento en diferentes escenarios:
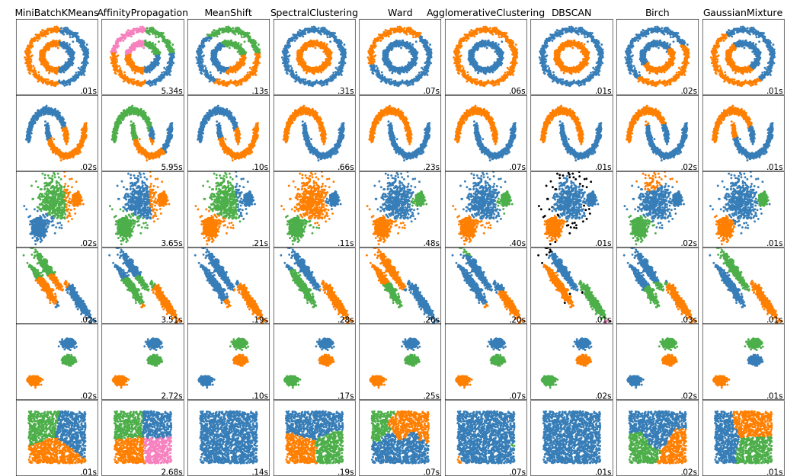
Fuente: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/clustering.html
E información sobre cada uno de ellos extraída de la misma página web:
| Method name | Parameters | Scalability | Usecase | Geometry (metric used) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-Means | number of clusters | Very large n_samples, medium n_clusters with MiniBatch code | General-purpose, even cluster size, flat geometry, not too many clusters | Distances between points |
| Affinity propagation | damping, sample preference | Not scalable with n_samples | Many clusters, uneven cluster size, non-flat geometry | Graph distance (e.g. nearest-neighbor graph) |
| Mean-shift | bandwidth | Not scalable with n_samples | Many clusters, uneven cluster size, non-flat geometry | Distances between points |
| Spectral clustering | number of clusters | Medium n_samples, small n_clusters | Few clusters, even cluster size, non-flat geometry | Graph distance (e.g. nearest-neighbor graph) |
| Ward hierarchical clustering | number of clusters | Large n_samples and n_clusters | Many clusters, possibly connectivity constraints | Distances between points |
| Agglomerative clustering | number of clusters, linkage type, distance | Large n_samples and n_clusters | Many clusters, possibly connectivity constraints, non Euclidean distances | Any pairwise distance |
| DBSCAN | neighborhood size | Very large n_samples, medium n_clusters | Non-flat geometry, uneven cluster sizes | Distances between nearest points |
| Gaussian mixtures | many | Not scalable | Flat geometry, good for density estimation | Mahalanobis distances to centers |
| Birch | branching factor, threshold, optional global clusterer. | Large n_clusters and n_samples | Large dataset, outlier removal, data reduction. | Euclidean distance between points |